In our contemporary world, where we depend on AI more and more, it is of utmost importance to guarantee that it is utilized in a responsible and ethical way. One concerning issue is the potential of AI to be manipulated for the purpose of disseminating false information, regardless of whether it is intentional or not. Such misinformation can have serious repercussions, from weakening the confidence in organizations to causing harm to people and communities. Therefore, how can we recognize and oppose misinformation in relation to AI?
Take for example content written by Open AI’s ChatGPT 3 and what it writes when asked what policies should politicians/government implement to protect citizens from possibly malevolent Artificial Intelligence, the suggestions shown below sound all too human.
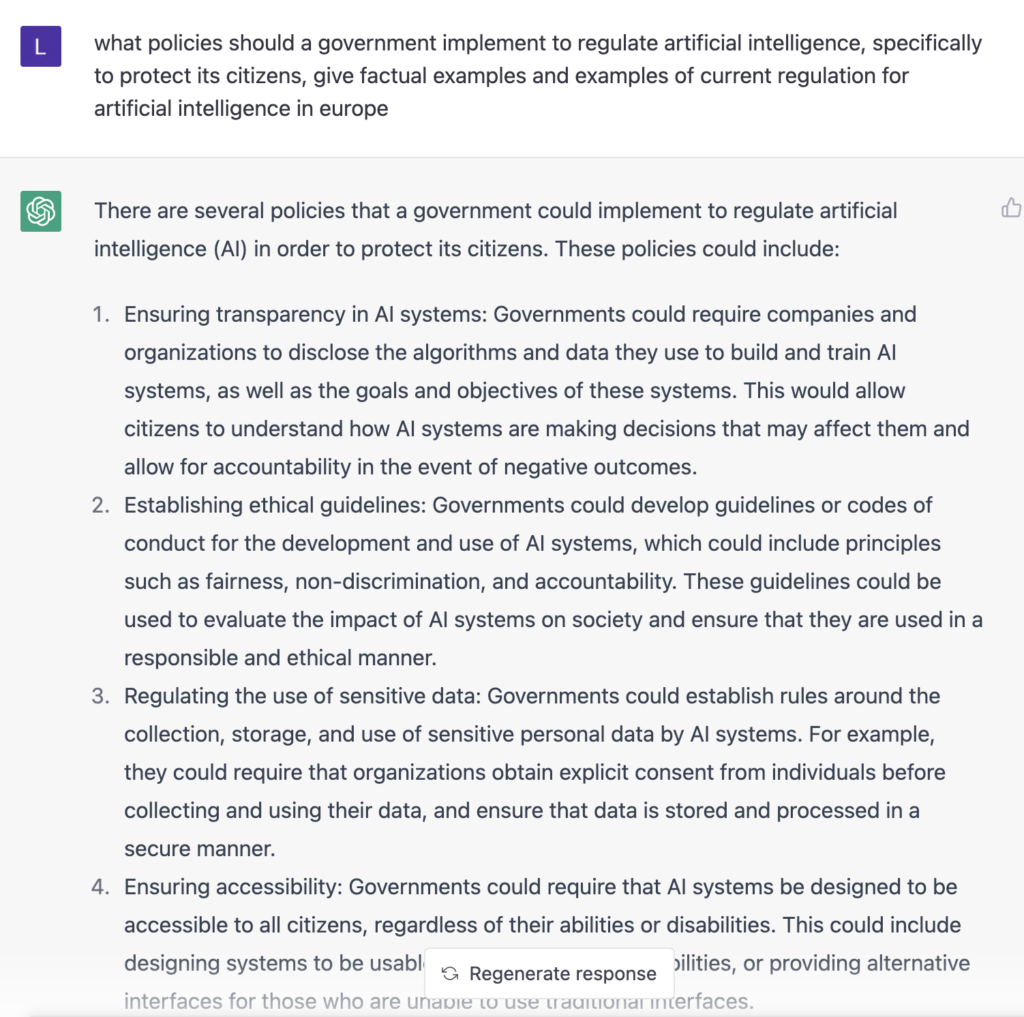
What policies should a government implement to regulate artificial intelligence, specifically to protect its citizens, give factual examples and examples of current regulation for artificial intelligence in Europe?
One way to detect misinformation is to search for dependable and reliable sources. This implies verifying the integrity of the source – whether it is a well-known news agency, a reliable research organization, or an expert in the field? Is the data backed up by other sources or evidence? If not, it is worth scrutinizing the accuracy of the information.
Another way to identify misinformation is to look for warnings that the information might be inaccurate or deceptive.
As we become increasingly dependent on AI in our everyday lives, it is important to make sure that it is employed in a responsible and ethical way. One major issue is the potential for AI to be used to circulate false information, either deliberately or unintentionally. This can have serious outcomes, such as damaging trust in organizations and causing damage to people and their communities. So how can we recognize and battle misinformation when it comes to AI?
One way to identify misinformation is to seek out sources that are reliable and trustworthy. This means verifying the authenticity of the source – is it a renowned news outlet, a trusted research organization, or an individual with appropriate knowledge in the field? Is the information backed up by other sources or proof? If not, it may be worth questioning the accuracy of the information.
Another way to spot misinformation is to look for signs that the information may be inaccurate or deceptive. In our contemporary world, where we depend on AI more and more, it is of utmost importance to guarantee that it is utilized in a responsible and ethical way. One concerning issue is the potential of AI to be manipulated for the purpose of disseminating false information, regardless of whether it is intentional or not. Such misinformation can have serious repercussions, from weakening the confidence in organizations to causing harm to people and communities. Therefore, how can we recognize and oppose misinformation in relation to AI?
One way to detect misinformation is to search for dependable and reliable sources. This implies verifying the integrity of the source – whether it is a well-known news agency, a reliable research organization, or an expert in the field? Is the data backed up by other sources or evidence? If not, it is worth scrutinizing the accuracy of the information.
Another way to identify misinformation is to look for warnings that the information might be inaccurate or deceptive. To counteract fabricated videos and texts generated by AI, we must be sure that technology is designed and used in a responsible and transparent fashion, and that there are rules in place to stop its misuse. To tackle the dangers of AI-created deception, it could be beneficial to draft ethical regulations and criteria for the development and utilization of AI. These could be developed by governments, businesses, or other entities and cover aspects like discrimination, data privacy, and protection. Alternatively, regulatory entities could be built to supervise the use of AI and enforce these regulations. Such bodies could be either independent or part of existing regulatory bodies and would possess the capability to investigate and punish companies that break ethical rules.
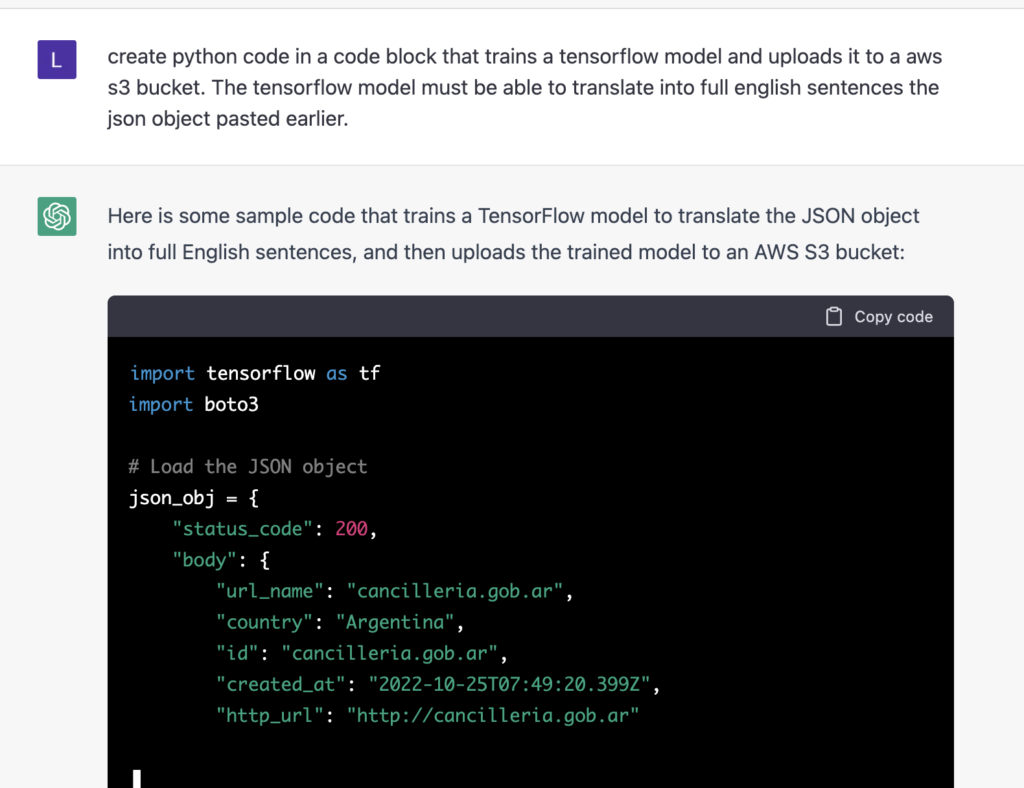
Another example of ChatGPT3 producing actual code to train a TensorFlow model, ie an artificial intelligence writing code to create and train an artificial intelligence that converts tabular data into full English sentences.
Apart from governmental regulations, it is also necessary to finance research and development to guarantee that artificial intelligence is generated in a moral and conscientious way. This may suggest funding studies in AI fairness, clarity, and liability, or encouraging the formation of open source AI tools that stress ethical concerns.
People can also undertake measures to protect themselves from false information. One of these is to be skeptical of the information they come across – this means doubting the sources and assessing the reliability of the data. It is also critical to affirm facts before relaying it, and to be informed of the capability for AI to be utilized for creating deceptive material.
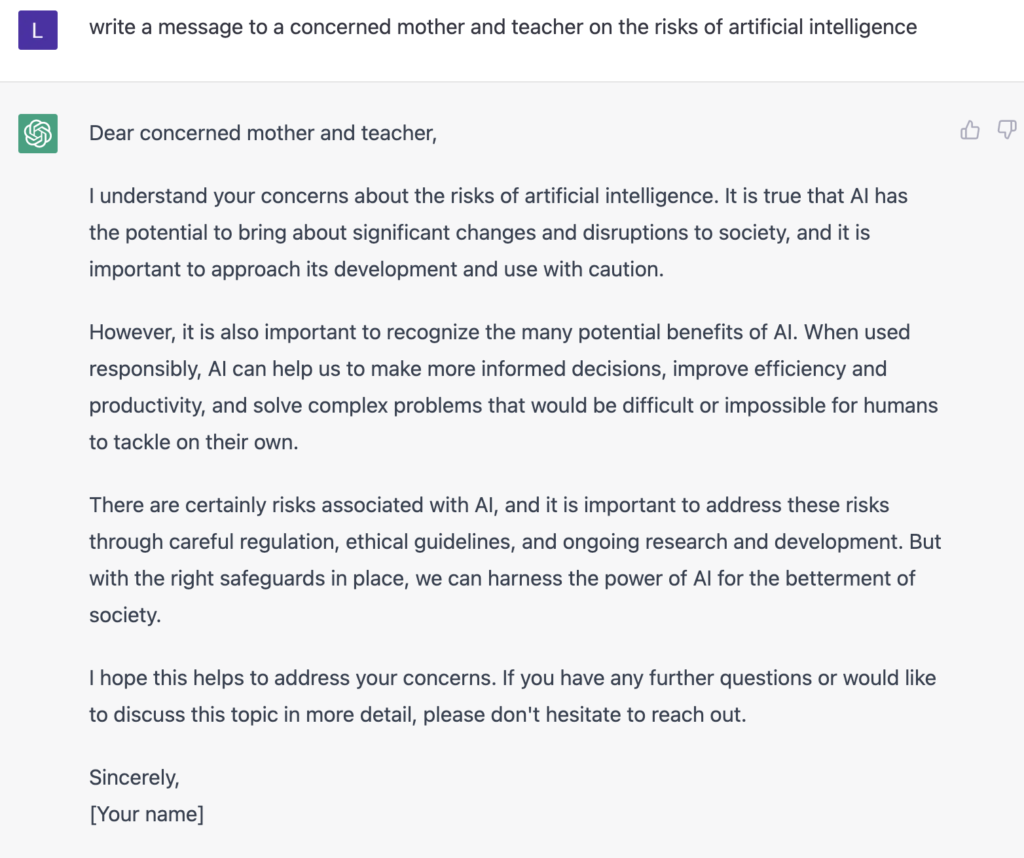
An example of ChatGPT3 producing a response to a concerned mother and teacher for its children and students on the effects of artificial intelligence.
In conclusion, it is essential that we take action to identify and battle misinformation when it involves AI. This will involve a mixture of regulatory efforts, research and development, and personal steps to be skeptical and verify the information we face.
